Navigating the complexities of student loan repayment can be daunting, especially when understanding the nuances of grace periods. This comprehensive guide will clarify what a grace period is, how it impacts your student loan payments, and what happens if you fail to meet your payment obligations during or after this period. We’ll explore the various types of grace periods offered by different loan servicers and provide actionable advice to help you effectively manage your student loan debt and avoid potential pitfalls.
Understanding your grace period is crucial for responsible student loan management. This period offers a temporary reprieve from student loan payments after graduation or leaving school, allowing you time to transition into a new phase of life and secure employment. However, it’s important to know that grace periods are not indefinite and ignoring them can have serious financial repercussions, including late payment fees, a damaged credit score, and ultimately, default on your loans. This article will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate your grace period and successfully manage your student loans.
What Is a Grace Period?
A grace period is a period of time after you complete your studies (or leave school) before you are required to begin making payments on your student loans. This period allows you to transition into the workforce and establish a stable financial footing before assuming the responsibility of loan repayment.
The length of the grace period can vary depending on several factors, including the type of loan and your lender. Federal student loans typically offer a standard grace period, while private student loans may have shorter grace periods or no grace period at all. It is crucial to check your loan documents carefully to understand the specifics of your grace period.
During the grace period, interest may or may not accrue, depending on the loan type. Subsidized federal loans usually do not accrue interest during the grace period, while unsubsidized federal loans and most private student loans do. This means that the amount you owe will increase even though you aren’t making payments. Understanding whether or not interest accrues is important for effective financial planning.
Failure to begin repayment after the grace period expires can result in negative consequences, such as late payment fees, damage to your credit score, and potential loan default. It’s essential to stay informed about your grace period’s end date and plan accordingly to avoid these issues.
How Long It Usually Lasts
The length of a grace period on student loans varies depending on the type of loan and the lender. There’s no single, universally applicable grace period duration.
For federal student loans, the grace period is typically six months after you graduate, leave school (for reasons other than completing your education), or drop below half-time enrollment. This applies to most federal loan programs, including subsidized and unsubsidized loans.
However, it’s crucial to understand that certain circumstances might alter this standard grace period. For instance, some borrowers enrolled in income-driven repayment plans might have different grace period lengths or no grace period at all. Direct Consolidation Loans have a different grace period that depends on the grace period of the loans being consolidated.
Private student loans, on the other hand, have far more variable grace periods. These can range from zero months to several months, and the specific duration is determined by the terms outlined in your loan agreement. It’s essential to thoroughly review your loan documents to understand the exact length of your grace period if you have private student loans.
Therefore, determining the precise length of your grace period requires carefully examining the specific terms of your loan agreement. Contacting your lender directly is another reliable way to confirm the details of your grace period.
When Interest Starts Accruing
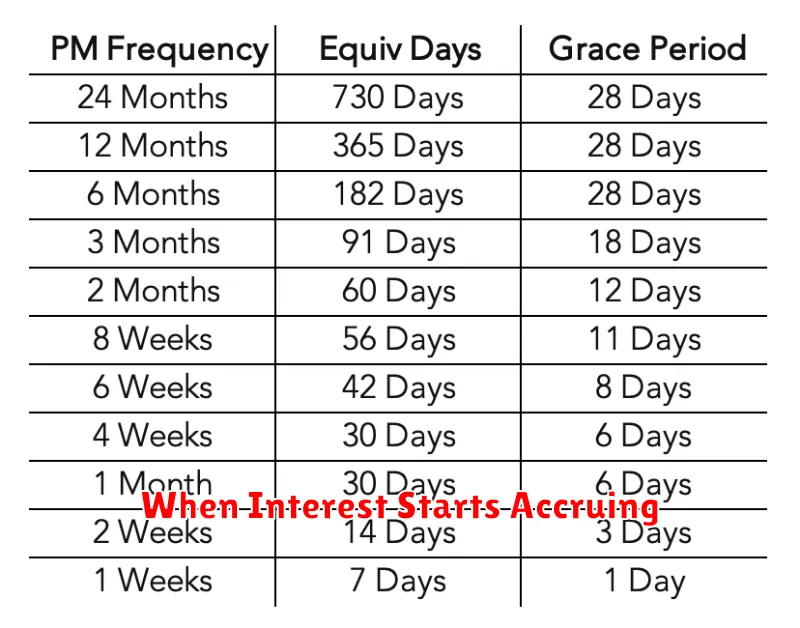
Understanding when interest begins to accrue on your student loans is crucial for effective financial planning. The timing depends largely on the type of loan and the presence of a grace period.
For many federal student loans, a grace period is provided after you graduate, leave school, or drop below half-time enrollment. This grace period typically lasts six months, during which time you are not required to make payments. However, it’s important to note that interest may still accrue during this grace period. This means that your loan balance will increase, even though you aren’t making payments. Your total interest paid will be higher if you wait until the end of your grace period to begin repayment.
Private student loans, on the other hand, often have different grace period policies. Some may offer a grace period, while others may require you to start making payments immediately upon the disbursement of the loan funds or after the completion of your studies. It’s essential to carefully review the terms and conditions of your specific private loan to determine when interest capitalization begins.
Furthermore, the interest rate significantly impacts the amount of interest that accumulates. A higher interest rate will result in faster growth of your loan balance during the grace period and throughout the repayment period. Therefore, understanding your interest rate is critical to managing your student loan debt effectively.
In summary, while a grace period can provide a temporary reprieve from repayment, it doesn’t eliminate the accrual of interest. Understanding the specifics of your loan agreement, including the length of your grace period and the applicable interest rate, will allow you to accurately estimate the total cost of your student loans.
Prepare Before the First Bill
Before your first student loan bill arrives, take proactive steps to ensure a smooth repayment process. This preparation will minimize stress and potential problems later on.
Understand your loan terms: Carefully review all loan documents, including the master promissory note. Pay close attention to the repayment plan you’ve chosen (e.g., standard, graduated, income-driven), the interest rate, and the total amount you owe. Knowing these details will help you budget effectively.
Set up automatic payments: Automating your payments is highly recommended. This prevents missed payments, which can negatively impact your credit score and potentially lead to late fees. Many lenders offer online portals for easy setup and management.
Create a budget: Factor your student loan payments into your monthly budget. Consider your other expenses, such as rent, utilities, and food, to ensure you can comfortably afford your loan payments without financial strain. If needed, explore options to reduce other expenses.
Explore repayment options: Familiarize yourself with different repayment plans available. Some plans offer lower monthly payments initially, but may lead to paying more interest over the loan’s lifetime. Consider your financial situation and long-term goals when choosing a plan.
Contact your lender: If you have any questions or concerns about your loan or repayment plan, don’t hesitate to contact your lender directly. They can provide clarification and support to help you navigate the repayment process.
Set Up Auto-Payment Reminders
To avoid late payments and the potential consequences, including late fees and a negative impact on your credit score, setting up auto-payment reminders is crucial. Many loan servicers offer this feature through their online portals or mobile applications.
Explore your servicer’s website or app to locate the settings for payment reminders. You’ll typically find options to receive email, text message, or even phone call reminders a few days before your payment is due. Customize the reminder frequency and method to best suit your preferences and schedule.
Consider using a personal calendar or reminder app in conjunction with your servicer’s system. This provides an additional layer of security, ensuring you receive multiple alerts and minimizing the risk of overlooking your payment due date. Set reminders well in advance, allowing ample time to process the payment before the deadline.
By proactively implementing auto-payment reminders, you can maintain a consistent payment history and avoid the potential financial penalties associated with late payments. This contributes to responsible debt management and strengthens your financial standing.
Budget Early to Avoid Delays
One of the most effective ways to avoid delays in your student loan repayment is to budget early and diligently. Creating a realistic budget well in advance of your grace period ending allows you to anticipate and plan for your monthly payments.
This proactive approach helps you avoid the stress and potential late payment fees associated with unexpected financial burdens. By tracking your income and expenses, you can identify areas where you might need to adjust your spending to accommodate your loan payments.
Consider using budgeting tools or apps to assist you in this process. These tools can help you visualize your finances, track your progress, and identify potential areas of overspending. Careful budgeting enables you to allocate sufficient funds for your loan payments without compromising other essential expenses.
Remember to factor in unexpected costs, such as car repairs or medical expenses, when creating your budget. Building a financial cushion can help you absorb these unexpected events without jeopardizing your ability to make timely loan payments.
Early and thorough budgeting is crucial for smooth loan repayment. It provides a clear financial roadmap, allowing you to navigate the transition from student to working professional with greater confidence and peace of mind.