Securing the best personal loan can feel overwhelming with numerous offers flooding the market. Understanding how to compare personal loan offers effectively is crucial to finding the most suitable and cost-effective financing solution for your needs. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities of personal loan interest rates, fees, and terms, ensuring you make a smart financial decision. We’ll break down the key factors to consider, helping you avoid costly mistakes and obtain the most favorable loan terms available.
Making a smart comparison of personal loan offers goes beyond simply looking at the advertised interest rate. We’ll delve into the importance of understanding APR (Annual Percentage Rate), analyzing loan fees, and evaluating the overall cost of borrowing. This detailed analysis will empower you to choose a personal loan that aligns perfectly with your budget and financial goals, avoiding hidden charges and ensuring you receive the best possible value for your money. Learn how to effectively assess and weigh different loan offers to ultimately secure the most beneficial financing option.
Compare APR, Tenure, and Total Cost
Choosing the right personal loan involves careful comparison of several key factors. Understanding and comparing the Annual Percentage Rate (APR), loan tenure, and the total cost of the loan are crucial steps in this process. These three elements work together to determine the overall financial implications of your loan.
The APR represents the annual cost of borrowing, including interest and any fees. A lower APR is always preferable, as it translates to lower overall interest payments. However, it’s essential to compare APRs from different lenders directly, as their calculation methods might vary slightly.
Loan tenure, or repayment period, significantly influences your monthly payments and the total interest paid. A shorter tenure means higher monthly payments but lower overall interest, while a longer tenure results in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest. Carefully consider your budget and financial capacity when selecting a loan tenure.
Finally, the total cost of the loan encompasses the principal amount borrowed plus the total interest accrued over the loan’s lifetime. This figure provides a clear picture of the total amount you will repay. By comparing the total cost across different loan offers, you can make an informed decision based on your ability to repay the loan comfortably.
To illustrate, consider two loan offers with the same principal amount: one with a lower APR but longer tenure, and another with a higher APR but shorter tenure. While the monthly payments might seem lower for the longer-tenure loan, the total cost could be significantly higher due to accumulated interest. Thorough comparison of these three factors—APR, tenure, and total cost—is essential for making a financially sound decision.
Watch Out for Hidden Fees
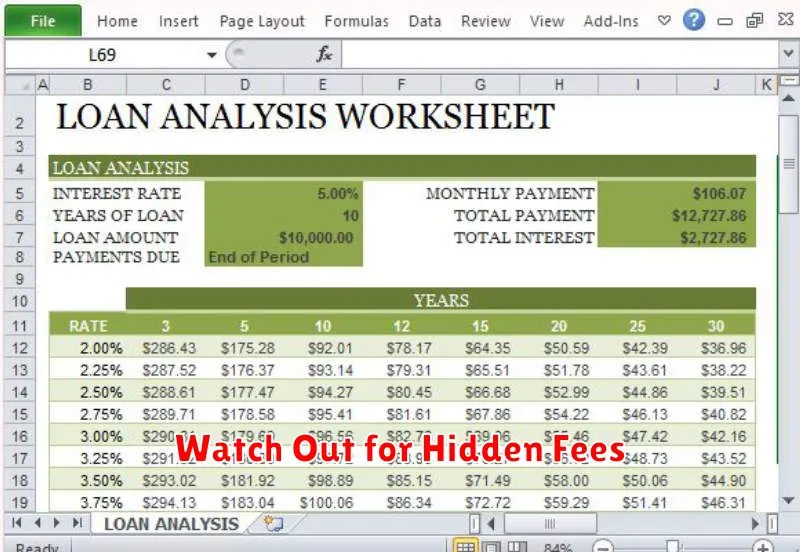
When comparing personal loan offers, it’s crucial to look beyond the advertised interest rate. Many lenders incorporate various fees that can significantly increase the total cost of your loan. These fees can easily inflate your monthly payments and overall loan amount.
Some common hidden fees include origination fees, which are charged for processing your loan application. Prepayment penalties can be levied if you pay off your loan early. Late payment fees are charged for missed or late payments, adding up quickly over time. Application fees may also be imposed simply for applying for the loan, regardless of approval.
Carefully review the loan agreement for a complete breakdown of all fees. Don’t hesitate to ask the lender for clarification if anything is unclear. Comparing the total cost of the loan, which includes all fees and interest, is more informative than solely focusing on the interest rate itself. A loan with a slightly higher interest rate but fewer fees might ultimately be a better deal than one with a lower interest rate but hefty hidden charges. Thorough investigation is essential to avoid unexpected expenses and ensure a cost-effective loan.
Understand Secured vs Unsecured Loans
When comparing personal loan offers, understanding the fundamental difference between secured and unsecured loans is crucial. This distinction significantly impacts your interest rate, loan amount, and overall borrowing experience.
A secured loan requires you to pledge an asset, such as a car or house, as collateral. If you default on the loan, the lender can seize and sell this asset to recover their losses. Because the lender assumes less risk, secured loans typically come with lower interest rates and larger loan amounts compared to their unsecured counterparts.
In contrast, an unsecured loan doesn’t require any collateral. The lender bases their decision solely on your creditworthiness. Since the lender bears a higher risk of non-repayment, unsecured loans generally have higher interest rates and smaller loan amounts. Your credit score plays a vital role in determining your eligibility and the terms offered.
Choosing between a secured and unsecured loan depends heavily on your individual circumstances and financial situation. Consider your credit score, the amount of money you need, and the assets you’re willing to risk before making a decision. Carefully weigh the pros and cons of each option to ensure you select the loan type that best suits your needs.
Check Prepayment and Late Penalties
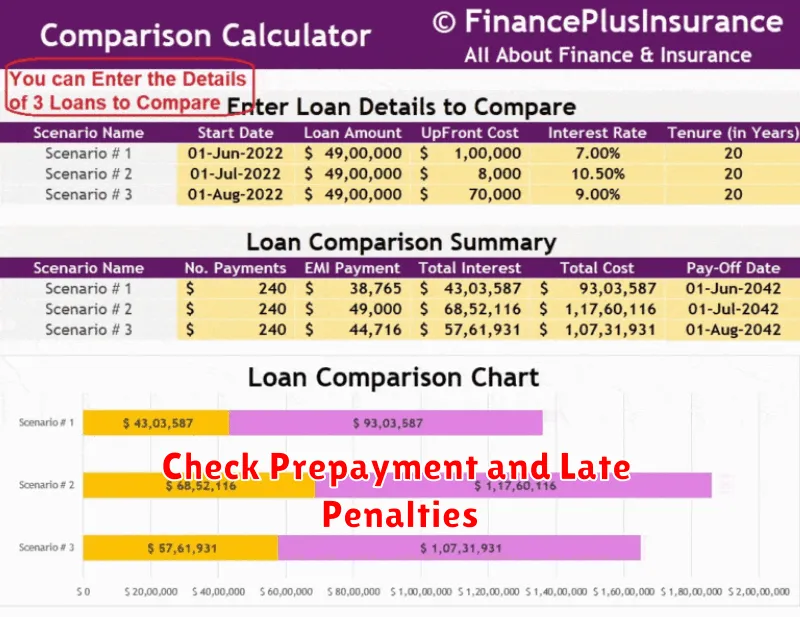
Before committing to a personal loan, carefully examine the terms related to prepayment penalties and late payment penalties. These fees can significantly impact the overall cost of your loan.
A prepayment penalty is a fee charged if you pay off your loan early. Some lenders include these penalties in their contracts, while others do not. If you anticipate the possibility of early repayment (e.g., receiving an unexpected bonus), choose a loan with either no prepayment penalty or a minimal one. Compare the potential savings from early repayment against any associated penalty.
Conversely, late payment penalties are charged when you miss a scheduled payment. These penalties can range from a fixed fee to a percentage of the missed payment, and can also negatively affect your credit score. Understand the exact penalty structure and ensure you can comfortably meet your monthly payment obligations to avoid incurring these charges. Consider your budget and repayment capabilities before selecting a loan with stringent late payment penalties.
Comparing these penalty structures across different loan offers is crucial for making an informed decision. Choose a loan with terms that align with your financial situation and risk tolerance. The absence of significant prepayment penalties offers flexibility, while manageable late payment penalties provide a safety net for unforeseen circumstances.
Evaluate the Reputation of the Lender
Before committing to a personal loan, it’s crucial to thoroughly investigate the lender’s reputation. A lender’s track record speaks volumes about their trustworthiness and how they treat their borrowers. A strong reputation is indicative of a reliable and ethical lending institution.
Begin by checking online reviews and ratings from reputable sources such as the Better Business Bureau (BBB). Look for patterns in customer feedback; consistently negative reviews should raise a red flag. Pay close attention to complaints regarding interest rates, fees, customer service responsiveness, and loan processing procedures. A high volume of negative reviews warrants further investigation or consideration of alternative lenders.
Consider researching the lender’s licensing and registration. Ensure they are properly licensed and authorized to operate in your state. You can usually find this information on the lender’s website or through your state’s financial regulatory agency. Operating without the necessary licenses is a major warning sign.
Investigate the lender’s financial stability. Check if they have a history of financial difficulties or bankruptcies. This information may be available through public records or financial news sources. A financially unstable lender may pose a greater risk, especially if your loan has a longer repayment term.
Finally, look for independent industry awards and recognitions. While not a definitive indicator of quality, awards can suggest a commitment to fair lending practices and customer satisfaction. However, always cross-reference this information with other research findings.
Read the Agreement Carefully
Before you sign on the dotted line for any personal loan, meticulously review the entire loan agreement. This seemingly tedious step is crucial to understanding the terms and conditions that govern your borrowing experience.
Pay close attention to the Annual Percentage Rate (APR). The APR represents the total cost of the loan, including interest and fees, expressed as a yearly percentage. A lower APR signifies a lower overall cost.
Scrutinize the loan fees. Many lenders charge various fees, such as origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment fees. Understanding these fees and their implications is paramount to budgeting effectively for loan repayment.
Carefully examine the repayment schedule. This outlines the monthly payment amounts and the total number of payments required. Ensure the repayment terms align with your financial capabilities and comfort level.
Thoroughly understand the terms of default. This section details the consequences of missing payments, such as late fees, potential damage to your credit score, and even legal action. Knowing these consequences will help you manage your loan responsibly.
Don’t hesitate to seek clarification if any terms or conditions are unclear. Contact the lender directly to ask questions and ensure complete comprehension before signing the agreement. Your understanding of the agreement is paramount to avoiding unforeseen financial difficulties.

